The Technology Blog

Biometric Data Privacy: Challenges and Solutions
Biometric security is a critical part of information safety in our digital era. Biometric technologies (e.g., fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, etc.) have become common in our daily interactions. However, this growth also raises significant privacy concerns about biometric data. The key is knowing the biometric privacy challenges. Reasonable solutions must be found for storing and securing data while addressing compliance.
Biometric privacy is crucial. These technologies constantly collect and store personal data, making them prime targets for cyber-attacks. Unlike passwords or PINs, biometric information is unique and cannot be changed if compromised. This blog will cover the challenges of biometric data privacy and suggest effective solutions to boost security and ensure compliance.
Key Benefits / Why It Matters

The Relevance of Biometric Privacy
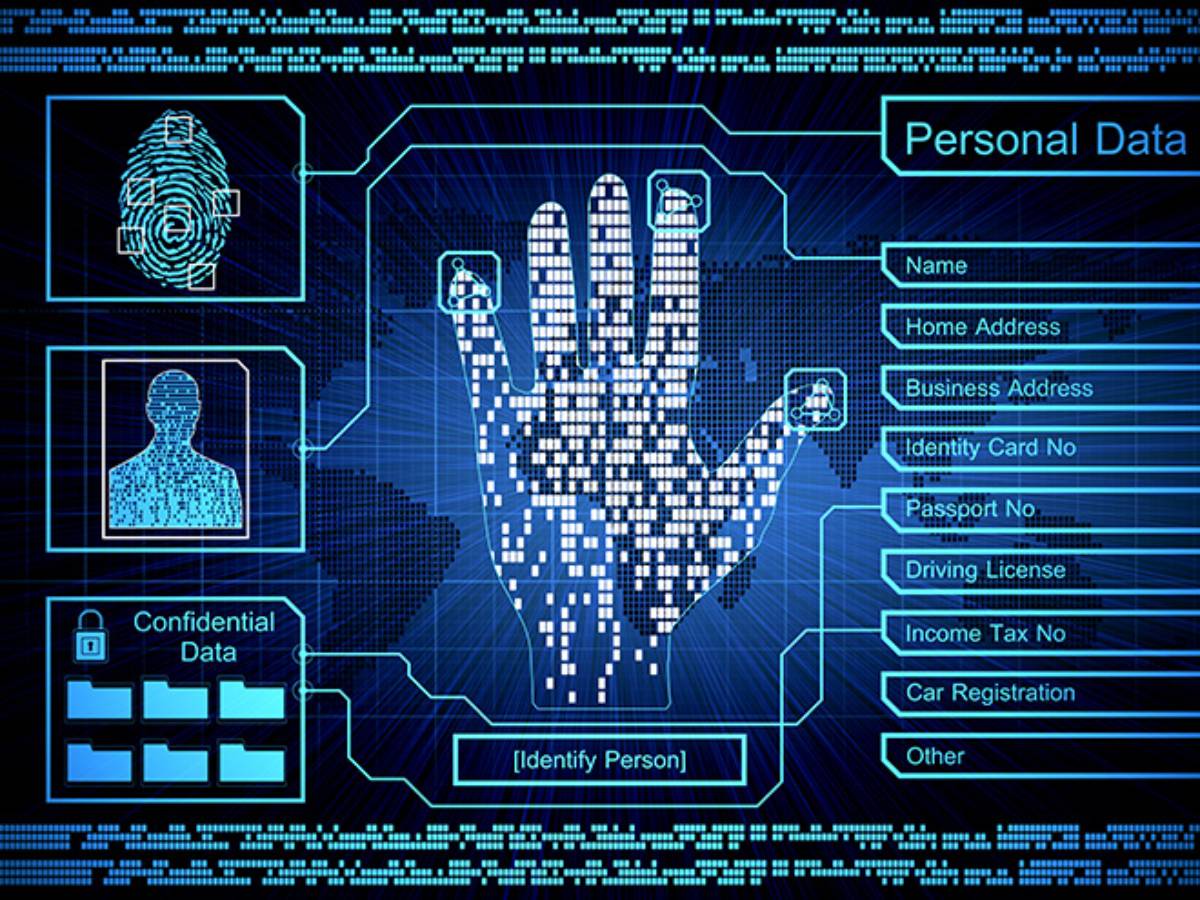
Biometric privacy is vital for modern data security. As technology can identify people by their unique traits, protecting this data is crucial. Biometric privacy matters for personal protection. It also shapes how much we trust organisations and technology.
Prioritising biometric privacy strengthens data security. When managed well, biometric systems can lower the risk of identity theft and fraud. Unlike passwords, biometric identifiers connect directly to a person, making them harder to steal. This connection provides a strong security layer in an age of advanced cyber threats.
Moreover, ensuring biometric privacy builds user trust. When individuals feel their data is secure, they are more likely to use new technologies. This trust drives growth and innovation in the biometric industry. Groups that focus on biometric privacy also follow strict data protection laws. This helps them avoid legal problems and fines.

Real-Life Applications and Data-Backed Insights
Biometric privacy matters in real-world applications across sectors. Biometric systems authenticate transactions in finance, offering a secure alternative to traditional methods. A study by Juniper Research shows that biometric authentication may protect over $2 trillion in transactions by 2023, highlighting its importance in financial security.
In healthcare, biometric systems improve patient identification, ensuring accurate matching of medical records. This boosts healthcare efficiency and protects sensitive patient data. An Accenture report predicts that biometric technology use in healthcare will grow by 22% each year, highlighting the need for strong privacy measures.
Additional Expert Tips & Common Mistakes to Avoid
Best Practices for Ensuring Biometric Privacy
Organisations should take a comprehensive approach to protect biometric data. Here are some tips:
- Implement Strong Encryption Protocols: Encrypting biometric data is crucial. Advanced encryption standards (AES) and public key infrastructure (PKI) are used to secure data in transit and at rest, making unauthorised access much more complicated.
- Adopt Privacy by Design Principles: Integrate privacy into developing biometric systems. Conduct risk assessments, minimise data collection, and ensure transparency in data handling.
- Update and Patch Systems Regularly: Always install the latest security updates and software patches for biometric systems. Regular audits and penetration testing help spot and fix vulnerabilities before exploitation.
- Educate and Train Employees: Human error can lead to data breaches. Training employees on biometric privacy and data security can lower accidental exposure risks.
Common Mistakes and Their Impact
Even with effort, organisations can still make mistakes that compromise biometric privacy. Knowing these pitfalls can help avoid them:
- Neglecting Data Retention Policies: If organisations don’t set clear data retention rules, they could collect too much biometric data. This can increase exposure risks. Set timeframes for data retention and securely dispose of data that no longer needs storage.
- Overlooking User Consent: Collecting biometric data without user consent can lead to legal issues and damage reputations. Obtain informed consent and give users control over their data.
- Inadequate Security Measures: Relying only on biometric systems without extra security, like multi-factor authentication, can leave data vulnerable. Layered security approaches offer added protection against breaches.
Advanced Insights / Expert Recommendations
Unique Industry Perspectives
As the biometric industry grows, experts advise a proactive approach to privacy. Stay updated on new technologies and regulations affecting data security. Collaborating with peers and participating in privacy forums can provide valuable insights and develop best practices.
Organisations should also explore using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance biometric security. AI can detect unusual behaviour patterns, alerting organisations to potential threats in real-time. Integrating AI and ML into biometric systems strengthens data security.
Additionally, as regulations evolve, ensure compliance with laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Following these laws protects user data and boosts an organisation’s credibility.
Biometric Privacy: Take First Steps
Understanding this concept is the basis of today’s data security and one of the burning topics in the future. But as biometric technologies proliferate, we need to solve the privacy issues they raise. Thus, security and compliance need to take a very strong stand. Best practices for organisations to secure biometric data: They must make special aids and not make the usual errors and scenarios. This helps build user trust.
In the days to come, organisations must stay aware of and take immediate action regarding biometric privacy concerns. Focusing on data security and compliance gives us the tools we need to use biometrics responsibly and safeguard privacy rights.
What steps will you take today to improve biometric privacy in your organisation? Share your thoughts and join the conversation on biometric data security.